Liver Cancer
Staging Systems
Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer
For staging HCC, the most commonly used system is the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer system (BCLC). It is based on three main factors:
- Tumor characteristics: size, how many tumors are present and whether the tumor(s) causes symptoms.
- The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status, which measures how the disease is affecting your ability to do daily activities. It is also a tool used to determine whether the cancer is progressing, potential treatment options and prognosis (outlook). It allows the doctor to better understand how you might tolerate treatment.
- The Child-Pugh score, a tool for evaluating how well the liver is working. This classification system uses five factors to determine the type of treatment that may be required:
- Albumin is a protein made by the liver.
- Bilirubin is a part of bile, which is made in the liver.
- Prothrombin time is a blood test to determine how quickly the blood clots. It is sometimes reported as International Normalized Ratio (INR).
- Ascites is an accumulation of fluid in the abdomen or legs.
- Encephalopathy indicates whether liver disease is affecting brain function.
Each of these factors is scored into a point system, which tallies the number of points to assign one of three classes:
- Class A: a well-functioning liver
- Class B: liver function is significantly compromised
- Class C: severe liver damage
Your doctor will combine the results from the three factors and classify the cancer into one of five BCLC stages from Stage 0 through Stage D. Stage 0 is very early-stage while Stage D is end-stage disease.
Stage 0 (very early stage): The tumor is less than 2 cm. The ECOG Performance Status is 0, meaning you are as active as before diagnosis. The Child-Pugh score is A, meaning the liver is working normally.
Stage A (early stage): There may be one lesion that is more than 2 cm, or there are up to three lesions that measure less than 3 cm. The ECOG Performance Status is 0, meaning you are as active as before diagnosis. The Child-Pugh score is A, meaning the liver is working normally or very close to normal despite underlying damage.
Stage B (intermediate stage): There may be more than one lesion with at least one that is more than 3 cm, or there are more than three lesions regardless of their size. The ECOG Performance Status is 0, meaning you are as active as before diagnosis. The Child-Pugh score is A, meaning the liver is working normally or very close to normal despite underlying damage.
Stage C (advanced stage): The cancer has invaded nearby blood vessels and/or has spread to lymph nodes and/or has spread to other parts of the body. The ECOG Performance Status is 1 to 2, meaning you may not be able to do heavy physical work but can do anything else, or you may be up about half the day and are unable to do any work activities. The Child-Pugh score is A, meaning the liver is working normally or very close to normal despite underlying damage.
Stage D (end-stage disease): The tumor may have grown into large blood vessels or spread to other parts of the body, and liver damage is severe. The ECOG Performance Score is 3 or 4, meaning you may be in bed or in a chair for more than half the day and you need help looking after yourself, or you are in bed or in a chair all the time and need complete care. The Child-Pugh score is B or C, meaning there is severe liver damage.
In addition, doctors may classify liver cancer based on whether it can be entirely resected (surgically removed) and may be described as the following:
- Localized resectable (confined to the liver and able to be surgically removed)
- Localized unresectable (confined to the liver but cannot be surgically removed)
- Advanced (has spread beyond the liver and likely cannot be treated with surgery)
BCLC Illustrated Stages of Liver Cancer
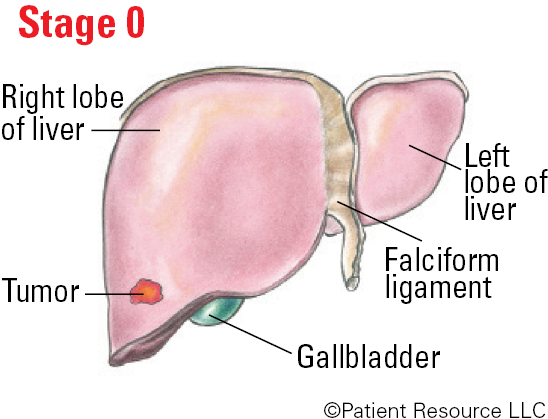
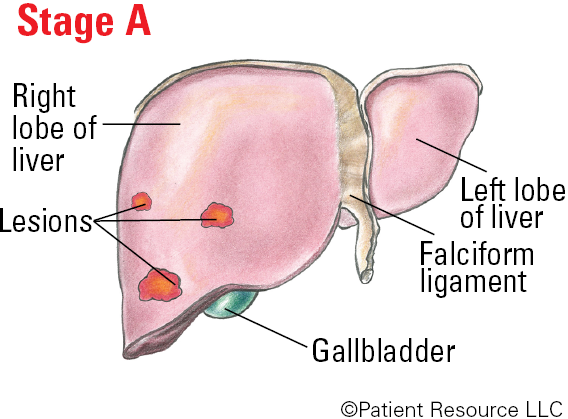

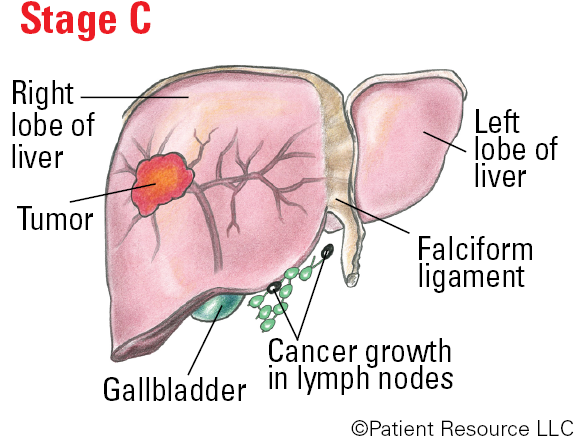
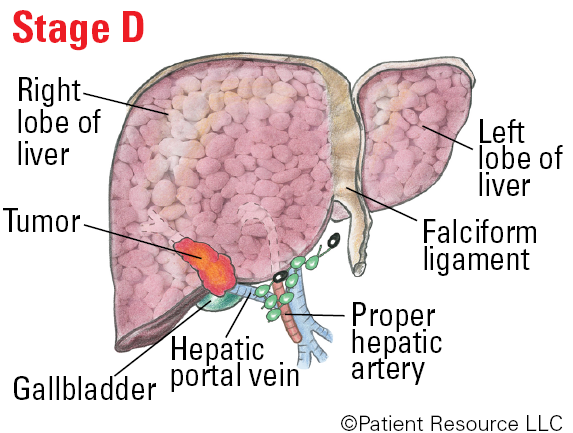
The Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) System
| BCLC Stage | Details |
| 0 (very early stage) |
|
| A (early stage) |
|
| B (intermediate stage) |
|
| C (advanced stage) |
|
| D (end-stage disease) |
|
Child-Pugh Scoring
| Clinical Measures | 1 point | 2 points | 3 points |
| Albumin (g/dL) | > (more than) 3.5 | 2.8-3.5 | < (less than) 2.8 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | < (less than) 2.0 | 2.0-3.0 | > (more than) 3.0 |
| Prothrombim time (in seconds) | < (less than) 4 | 4-6 | > (more than) 6 |
| INR | < (less than) 1.7 | 1.7-2.3 | > (more than) 2.3 |
| Presence of ascites | None | Moderate | Severe |
| Presence of hepatic encephalopathy | None | Grades I-II (or suppressed with medication) | Grades III-IV (or refractory) |
| Classification | Class A | Class B | Class C |
| Total points | 5-6 points | 7-9 points | 10-15 points |
| Indication | Indicates a well-functioning liver | Indicates liver function is significantly compromised | Indicates there is severe liver damage |
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status
| Grade | ECOG |
| 0 | Fully active, able to carry on all pre-disease performance without restriction |
| 1 | Restricted in physically strenuous activity but ambulatory and able to carry out work of a light or sedentary nature, e.g., light house work, office work |
| 2 | Ambulatory and capable of all self-care but unable to carry out any work activities; up and about more than 50% of waking hours |
| 3 | Capable of only limited self-care; confined to bed or chair more than 50% of waking hours |
| 4 | Completely disabled; cannot carry on any self-care; totally confined to bed or chair |
American Joint Committee on Cancer
The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM classification and staging system is used to determine the size of the main tumor and whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes and to distant parts of the body. This staging system is most commonly used in patients after they have undergone surgical removal of their tumor and the pathologist’s report is available. A stage is assigned that ranges from I to IV (see Figure 2). The higher the number, the more severe the disease.
The TNM system classifies the cancer based on four main categories: tumor (T), node (N) and metastasis (M), as well as whether the tumor is observed to have entered blood vessels. The T category describes the size and location of the primary tumor. The N category indicates whether the lymph nodes show evidence of cancer cells. The M category describes metastasis (spread of cancer to another part of the body), if any. The grade describes how abnormal the cancer cells and tissue look under a microscope and how likely they are to grow and spread.
The results of the TNM analysis are combined to determine the overall stage of the cancer. The liver cancer is then given one of the following four stages:
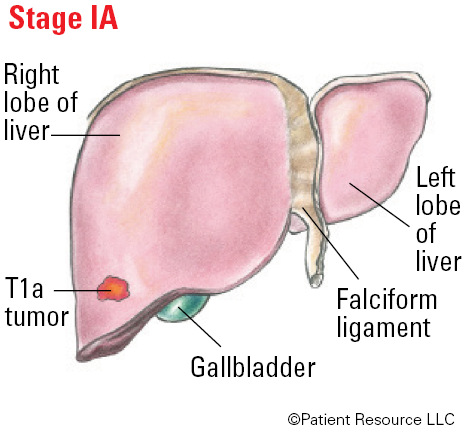
Stage I: A single tumor is confined to the liver.
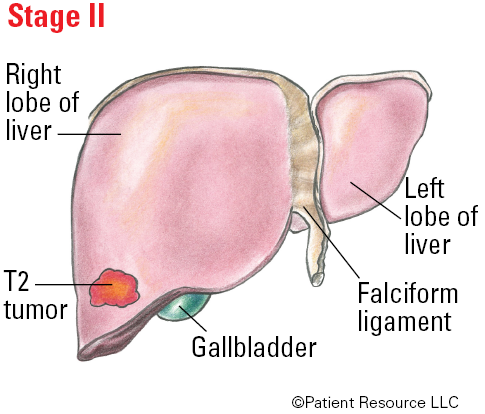
Stage II: A tumor larger than 2 cm and cancerous cells may have grown into nearby blood vessels.
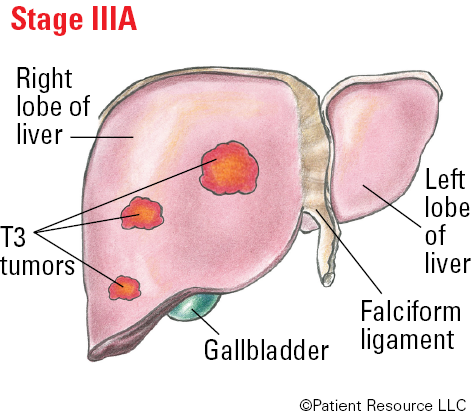
Stage III: Multiple tumors and/or growth into a major branch of the main blood vessels of the liver.
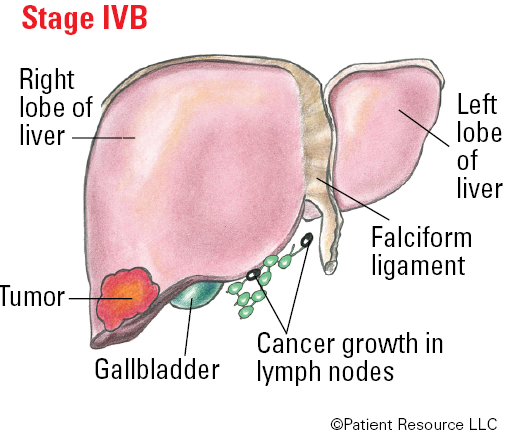
Stage IV: The tumor(s) may be any size and has spread to regional lymph nodes and/or distant parts of the body.
AJCC - Illustrated Stages of Liver Cancer

AJCC TNM System for Classifying Liver Cancer
| Category | Definition |
| Tumor (T) | |
| TX | Primary tumor cannot be assessed. |
| T0 | No evidence of a primary tumor. |
| T1 | Solitary tumor is not more than 2 cm, or more than 2 cm without vascular incasion |
| T1a | Solitary tumor not more than 2 cm. |
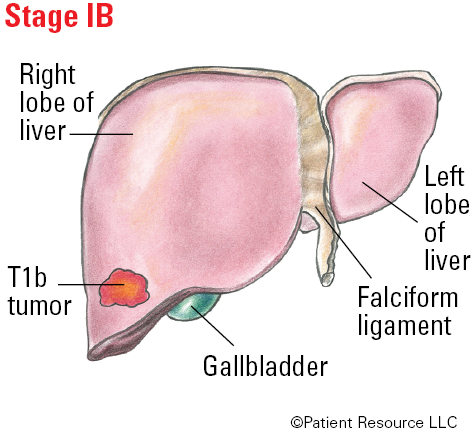
| T1b | Solitary tumor more than 2 cm without vascular invasion. |
| T2 | Solitary tumor more than 2 cm with vascular invasion, or multiple tumors, none more than 5 cm. |
| T3 | Multiple tumors, at least one of which is more than 5 cm. |
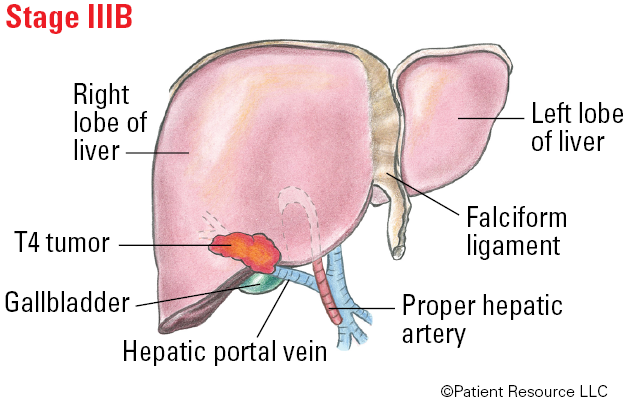
| T4 | Single tumor or multiple tumors of any size involving a major branch of the portal vein or hepatic vein, or tumor(s) with direct invasion of adjacent organs other than the gallbladder or with perforation of visceral peritoneum (outer layer of the liver). |
| Nodes (N) | |
| NX | Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed. |
| N0 | No regional lymph node metastasis. |
| N1 | Regional lymph node metastasis. |
| Metastasis (M) | |
| M0 | No distant metastasis. |
| M1 | Distant metastasis. |
| Grade (G) | |
| GX | Grade cannot be assessed. |
| G1 | Well-differentiated. |
| G2 | Moderately differentiated. |
| G3 | Poorly differentiated. |
| G4 | Undifferentiated. |
Stages of Liver Cancer
| Stage | T | N | M |
| IA | T1a | N0 | M0 |
| IB | T1b | N0 | M0 |
| II | T2 | N0 | M0 |
| IIIA | T3 | N0 | M0 |
| IIIB | T4 | N0 | M0 |
| IVA | Any T | N1 | M0 |
| IVB | Any T | Any N | M1 |



